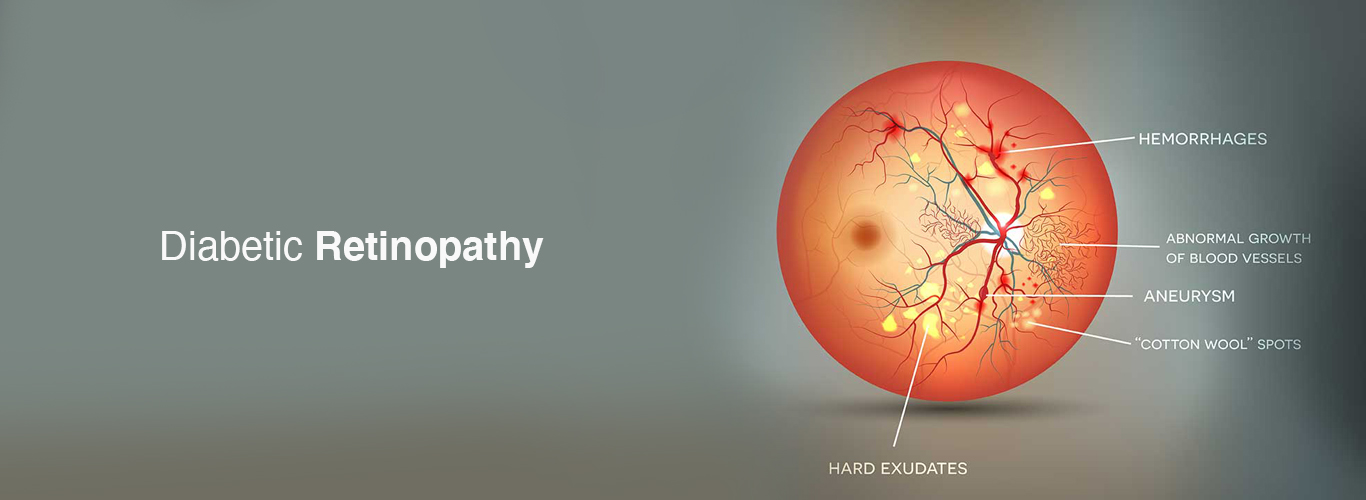
Hypertension:
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a global health concern affecting a significant portion of the adult population. This blog aims to provide an overview of essential hypertension, including its symptoms, causes, complications, and available treatments.
Prevalence and Awareness:
- It is estimated that 1.28 billion adults aged 30-79 worldwide have hypertension, with two-thirds residing in low- and middle-income countries.
- Surprisingly, around 46% of adults with hypertension are unaware of their condition.
- Only 42% of adults diagnosed with hypertension receive appropriate treatment.
- Alarmingly, just 21% of individuals with hypertension have their blood pressure under control.
Overview of Hypertension:
Hypertension is defined as having blood pressure levels equal to or higher than 140/90 mmHg. Although it is a common condition, it can lead to severe complications if left untreated. Notably, individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms, emphasizing the importance of regular blood pressure check-ups.
Risk Factors of Hypertension:
Several factors contribute to an increased risk of developing hypertension, including:
- Advancing age
- Genetic predisposition
- Overweight or obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Excessive salt consumption
- Heavy alcohol consumption
Symptoms of Hypertension:
Hypertension is often referred to as the “silent killer” due to its asymptomatic nature. However, extremely high blood pressure levels can manifest symptoms such as severe headaches, chest pain, dizziness, difficulty breathing, and blurred vision. Immediate medical attention is necessary for individuals experiencing these symptoms alongside high blood pressure readings.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Hypertension is diagnosed when repeated blood
pressure measurements show systolic readings ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic readings ≥90 mmHg. The primary focus of treatment involves lifestyle modifications and, if necessary, medication. Recommendations for managing hypertension include:
- Adopting a healthy, low-salt diet
- Weight reduction for overweight individuals
- Regular physical activity
- Smoking cessation
- Medication, if prescribed by a healthcare professional
Prevention:
Prevention plays a vital role in managing hypertension. Incorporating the following lifestyle changes can help prevent and control high blood pressure:
Increasing consumption of fruits and vegetables
- Engaging in regular physical activity, both aerobic and strength-building exercises
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Complying with prescribed medication
- Attending scheduled medical appointments
Complications:
Uncontrolled hypertension can lead to serious complications, including:
- Damage to the heart, potentially causing chest pain, heart attack, heart failure, or irregular heart rhythm.
- Increased risk of stroke due to arterial blockage or rupture in the brain.
- Kidney damage, potentially leading to kidney failure.
Conclusion:
Essential hypertension poses a significant health risk worldwide, with a substantial number of individuals remaining undiagnosed and untreated. Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and complications associated with hypertension is crucial for effective management. By implementing lifestyle changes, seeking timely medical attention, and adhering to prescribed treatments, individuals can reduce the impact of hypertension on their overall health and well-being.