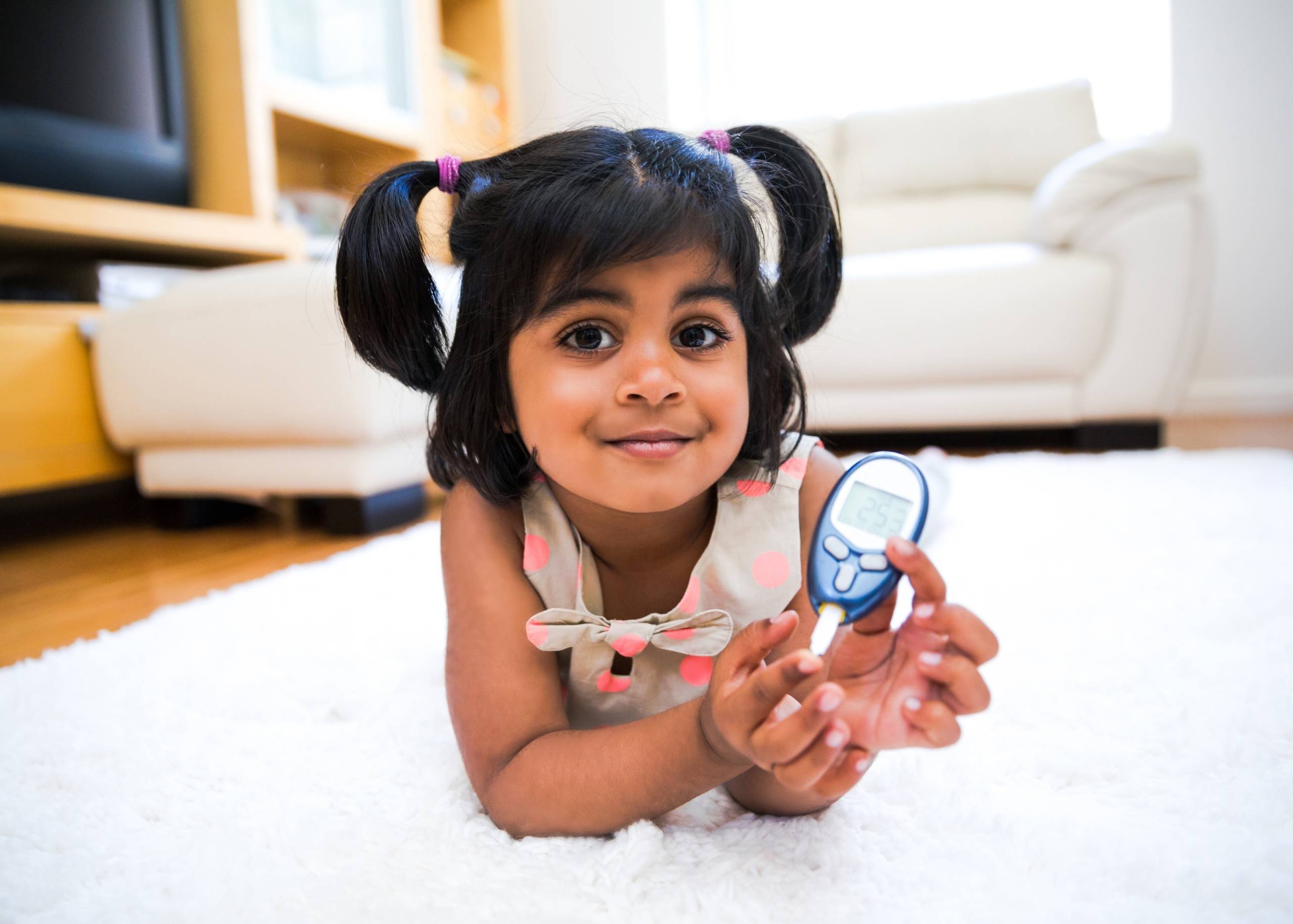
Type 1 diabetes is an auto-immune disease in which the body does not produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. This can lead to high blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia), which can cause serious health problems if left untreated. It can be caused by genetics, environmental triggers, and autoimmune disorders. The condition usually begins in childhood or young adulthood and may last throughout your life. To control blood sugar levels, you must take insulin injections regularly and carefully manage your diet.
What Causes Type 1 Diabetes?
It is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Insulin is a hormone that helps control blood sugar levels.
When you eat, your body breaks down food into glucose (a type of sugar), which enters your bloodstream and raises blood sugar levels.
However, if you have the condition, your body cannot make enough insulin to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
The cause is unknown. It appears that some combination of genetics and environmental factors (such as viruses) triggers the disease.
What are the Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes?
In the early stages, symptoms may not be noticeable, but they can include the following:
- Increased hunger and thirst
- Urination frequency
- Extreme fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Irritability or mood swings
- Frequent infections
What are the Risk Factors?
The most common risk factors include:
Age – Children under the age of 10 are at greater risk for developing the condition because their bodies haven’t yet fully developed the ability to produce insulin.
Family History – If your family has a history of type 1 diabetes, you may be more likely to develop it yourself.
Genetics – If you have certain genetic markers for type 1 diabetes, you may be at higher risk of developing it than someone without those markers.
What are the Treatments Available?
It is a lifelong condition affecting how your body metabolizes glucose and produces insulin.
The goal of the treatment is to manage your blood sugar levels through diet and exercise, as well as regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels and administering insulin shots.
The most important aspect of treating Type 1 Diabetes is maintaining a healthy diet and exercising regularly. A healthy diet can help you regulate your blood sugar levels, while exercise gives you more energy to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
It is an autoimmune disease that results in the body’s immune system attacking the cells that produce insulin. The team of board-certified physicians, nurses, and other health care professionals at LLH Hospital, Abu Dhabi, specializing in the treatment of type 1 diabetes and will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets your needs,