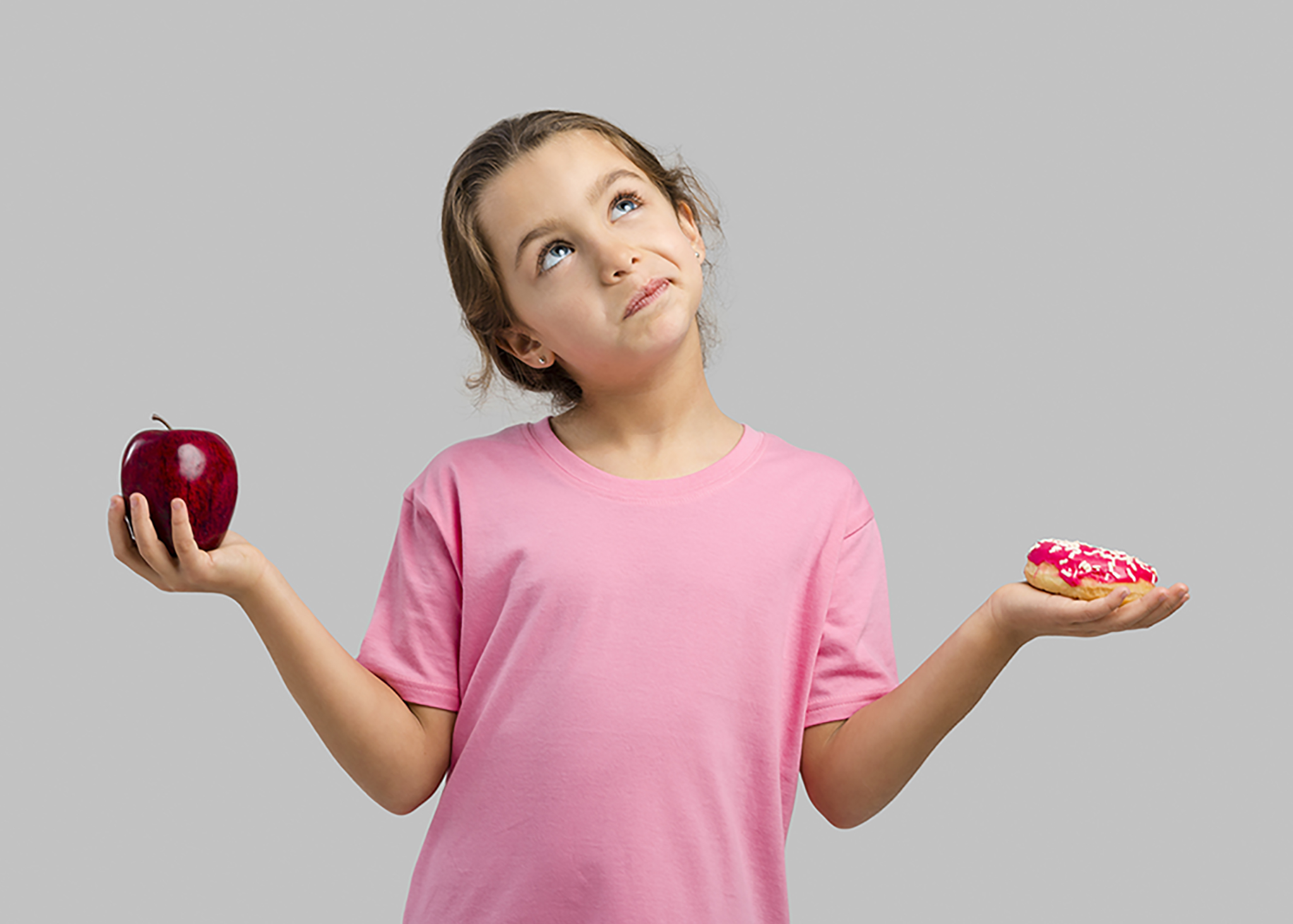
Childhood overweight and obesity have become a pressing public health issue, with a significant rise in global prevalence over the past four decades. Worldwide, more than 340 million children and adolescents aged 5 to 19 suffer from obesity, while 39 million children under the age of 5 are affected. UAE also witnessed an increase in incidence of childhood obesity from12 percent of children in 2018 to 17.4 percent in 2020 .This blog explores the causes, implications, and actionable steps parents can take to address childhood obesity in the UAE.
The Growing Concern of Childhood Obesity:
Childhood obesity is defined as the abnormal or excessive accumulation of fat that poses health risks. It is determined using Body Mass Index (BMI), adjusted for age and sex due to BMI changes during growth. For ages 2 to 19, overweight is classified as having a BMI between the 85th and 95th percentiles, while obesity is defined as a BMI at or above the 95th percentile. Early life is a critical period for obesity development, as the environment during this stage can influence health outcomes later in life.
Factors Contributing to Childhood Obesity:
The rise in childhood obesity can be attributed to various behavioral and environmental factors. Increased screen time, inadequate sleep, reduced physical activity, and the consumption of energy-dense, nutrient-poor foods play significant roles. Additionally, prenatal and postnatal factors, as well as genetic variations, contribute to the development of childhood obesity. The shift towards ultra-processed foods, high intake of sugary beverages, and a decrease in physical activity further compound the issue.
Implications and Risks of Childhood Obesity:
Childhood obesity is associated with numerous short-term co-morbidities, including impaired glucose tolerance, delayed or accelerated puberty, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, altered lipid levels, dental caries, and various other health complications. Children with obesity may also face social rejection and victimization. Furthermore, childhood obesity tends to persist into adolescence and adulthood, increasing the risk of long-term complications such as adult obesity, coronary artery disease, infertility, osteoarthritis, reduced self-esteem, depression, anxiety, and impaired motor skills.
Addressing Childhood Obesity:
If parents suspect their child is obese, seeking guidance from healthcare professionals is crucial. BMI serves as a screening tool, but it should be supplemented by clinical assessment. Parents can support their child’s health by focusing on positive behaviors rather than deprivation. Providing nutritious meals and snacks filled with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is essential. Building self-esteem and shifting the conversation away from weight numbers to health promotion can also contribute to positive outcomes.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Parents can serve as role models by adopting healthy eating patterns for the entire family. Involving children in shopping for fresh produce and meal planning fosters their engagement. Eating meals together without screen time and avoiding the consumption of “JUNCS” (foods high in fats, sugars, and salts, ultra-processed foods, nutritionally inappropriate foods, and sugar-sweetened beverages) are crucial steps. Limiting the intake of free sugars and fats, encouraging regional and seasonal fruit consumption, and promoting physical activity are essential for combating childhood obesity.
Limiting Screen Time and Other Treatment Options:
To curb sedentary behavior, parents should limit screen time to less than two hours per day for children above 5 years old. For children aged 2 to 5, screen time should be limited to less than one hour, while children under 2 should have zero screen time. In severe cases of adolescent obesity, where conventional treatments are ineffective, intensive dietary interventions, medications, or bariatric surgery may be considered.
Conclusion:
Childhood obesity poses significant health risks and long-term consequences. Parents play a vital role in promoting healthy habits and creating a supportive environment for their children. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals can provide trusted advice and support. Dr. Gopika Prasad, Specialist in General Pediatrics, emphasizes, “Addressing childhood obesity requires a comprehensive approach that involves healthy nutrition, regular physical activity, and a supportive family environment. It’s important for parents to lead by example and provide their children with the tools and resources they need to make positive lifestyle choices.”
By adopting nutritious eating patterns, encouraging physical activity, and limiting sedentary behavior, parents can contribute to their child’s overall well-being and future health. Together, with the guidance of healthcare experts like Dr. Gopika Prasad, we can combat childhood obesity and ensure a healthier future for the children of the UAE. Remember, as Dr. Prasad advises, “Small changes can make a big difference in preventing and managing childhood obesity. Let’s work together to give our children a healthy start in life.”